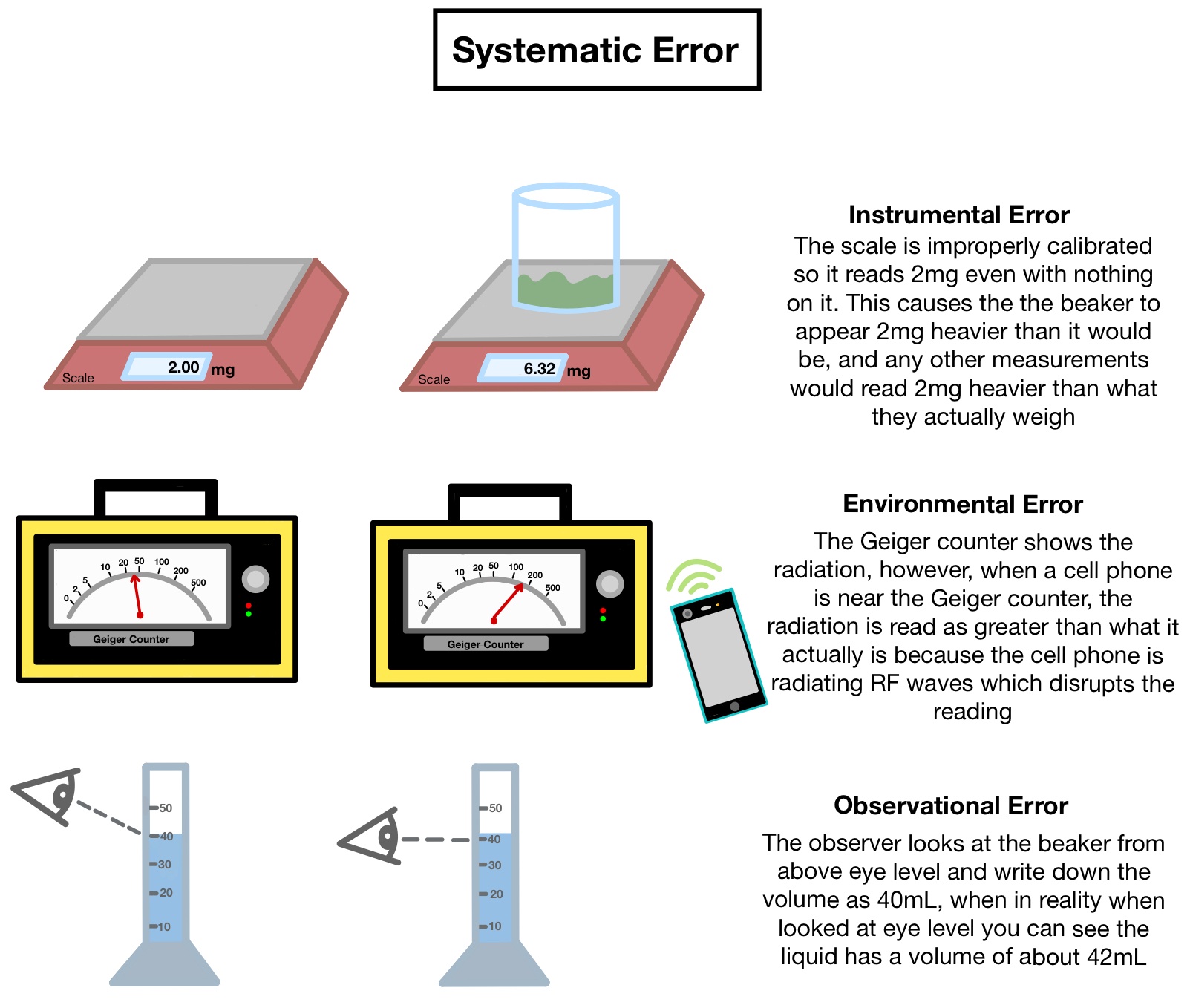
Systematic Error | Error Analysis Biology For Life
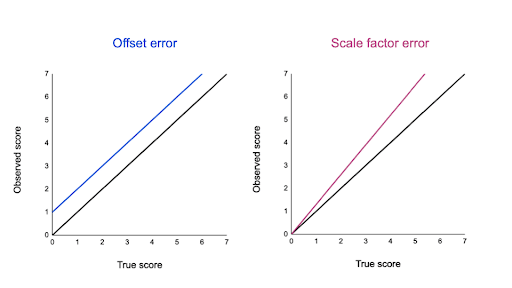
The amount by which the value differs from the true value may be a constant. Such a situation would occur for example when using a micrometer that has a zero error.
Types Of Error Overview Comparison Expii
Learn more about our Physics Term Course.
Systematic error. A systematic error is one that results from a persistent issue and leads to a consistent error in your measurements. Systematic Errors Systematic errors are errors of measurements in which the measured quantities are displaced from the true value by fixed magnitude and in the same direction. Systematic error in physical sciences commonly occurs with the measuring instrument having a zero error.
The scale of the micrometer indicating a non-zero value when the jaws of the micrometer are closed. Two types of systematic error can occur with instruments having a linear response. They may occur because.
The issue however is that systematic errors are not easily detectable. How to Minimize or Avoid Systematic Errors in Research. Systematic error is a consistent or proportional difference between the observed and true values of something eg a miscalibrated scale consistently records weights as higher than they actually are.
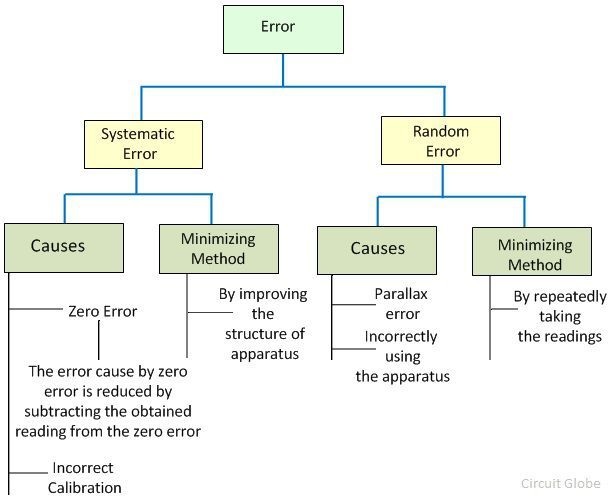
Once you can identify the cause of a systematic error you should be able to reduce its effect on your data to a great extent. Instrument errors - failure to calibrate degradation of parts in the instrument power fluctuations variation in temperature etc. A systematic error causes a measured value to be consistently greater or less than the true value.
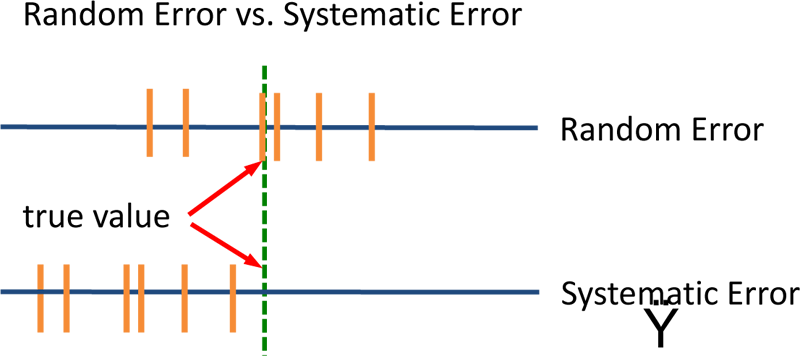
Definition of systematic error. Systematic vs Random errors. An error that is not determined by chance but is introduced by an inaccuracy as of observation or measurement inherent in the system.
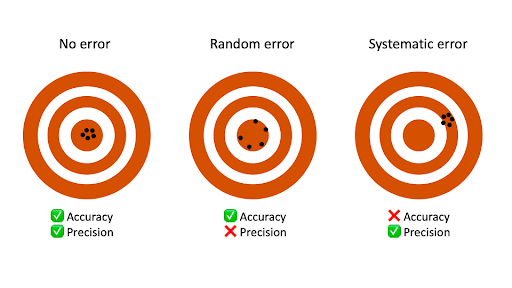
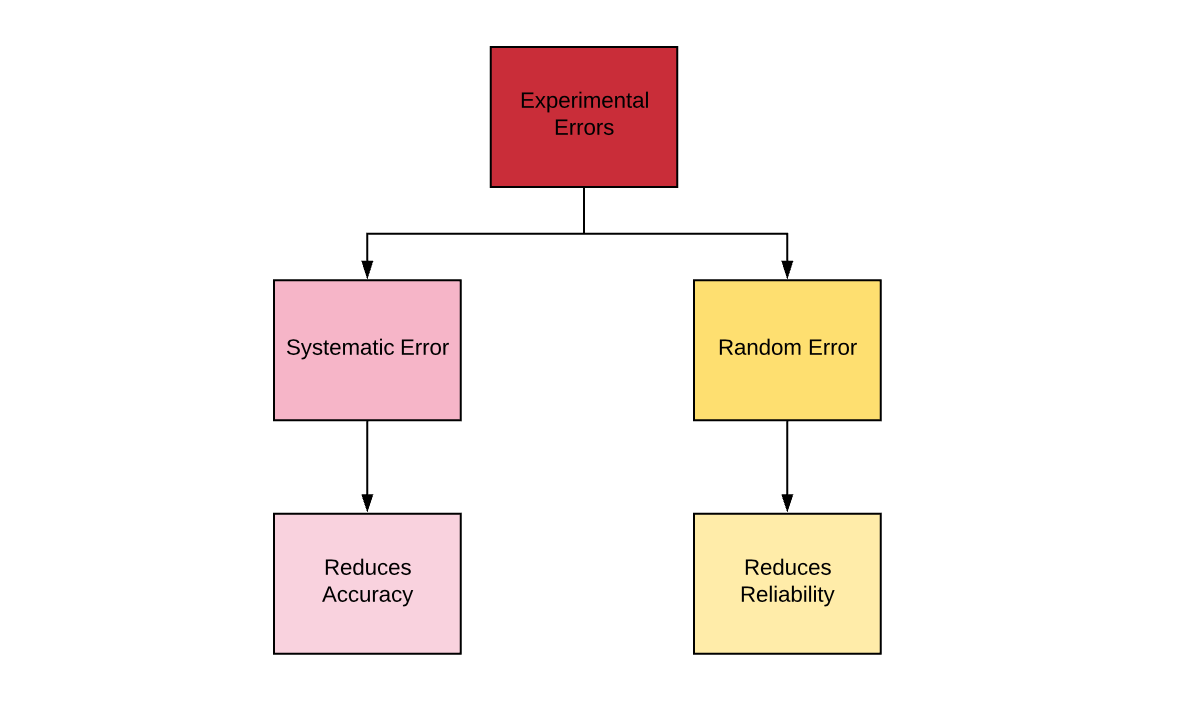
There is something wrong with the instrument or its data handling system or because the instrument is wrongly used by the experimenter. Systematic errors affect accuracy whereas random errors affect the reliability of experimental results. A zero error is when the initial value shown by the measuring instrument is a.
Gain an in-depth knowledge and understanding of an entire module before its taught in school. For example if your measuring tape has been stretched out your results will always be lower than the true value. Get a head start with your next Physics Practical Assessment.
Systematic Errors Systematic errors in experimental observations usually come from the measuring instruments. Can be corrected by calibration or proper instrumentation maintenance. A systematic error is any biasing effect in the environment methods of observation or instruments used which introduces error into an experiment and is such that it always affects the results of an experiment in the same direction.
Systematic Error Random Error Definition And Examples Statistics How To
Error Sources In Speciation Analysis Overview Evisa S News
4 Systematic Vs Random Errors The Nature Of Geographic Information

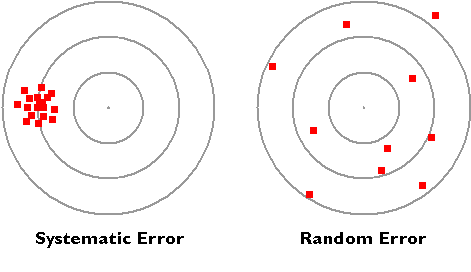
Systematic Vs Random Error Differences And Examples
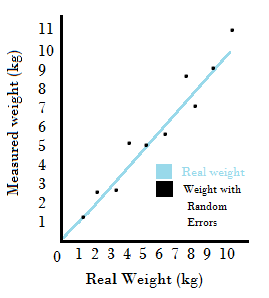
Random And Systematic Error Differences Sources Examples

Systematic Error An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Difference Between Random Systematic Error The Engineering Knowledge
Systematic Vs Random Errors In Physics Part 3 Of Physics Skills Guide

Random Vs Systematic Error Top 8 Differences With Infographics

Systematic Error Curie Metro High School

Measurement Error Types Of Error Difference Between Systematic Error Vrs Random Error Youtube
Difference Between Systematic Error And Random Error Difference Between

General Concepts In Biostatistics And Clinical Epidemiology Random Error And Systematic Error Medwave

Error Analysis Biology For Life
Random And Systematic Error Differences Sources Examples
Difference Between Random Systematic Error With Comparison Chart Circuit Globe
